下载中心
优秀审稿专家
优秀论文
相关链接
首页 > 2020年第6期封面报道
2020年第6期封面报道
新冠疫情期间中国地区大气二氧化氮浓度遥感监测
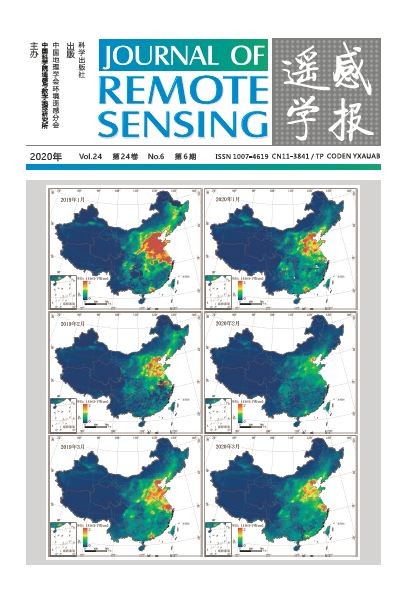
封面图片为搭载于美国Aura 卫星上的OMI 载荷监测的中国地区2020 年1 月、2 月及2019 年同期大气二氧化氮对流层柱浓度月均值分布图。卫星监 测结果表明2020 年2 月二氧化氮对流层浓度和工业热源企业耗能水平较同期均呈现显著下降趋势。在新型冠状病毒疫情得到基本控制之后,中国大部 分地区的工业热源企业虽已逐步有序地恢复生产,但复工区域仍处于低能耗水平,生产规模尚未完全恢复。利用卫星遥感技术监测来源于工业高温燃烧 以及机动车尾气的大气二氧化氮浓度变化及工业热源企业热排放变化,提供了一种新的视角反映工业活动与人们出行状态。相关研究结果详见第7 期第 824-836 页“新型冠状病毒疫情期间复工复产卫星遥感监测”(审图号:GS (2020) 1848 号)。
Satellite observations of NO2 over China during the period of COVID-19
The cover image shows the Aura/OMI monthly tropospheric NO2 Vertical Column Density (VCD) data over China during the periods
from January to February in 2020 and 2019, respectively. Satellite observations indicate that there are significant reductions of both
NO2 emission and industrial energy consumption in February 2020, compared to those of both January 2020 and February 2019. With
the abatement of COVID-19 in China, although many industrial factories started to re-open, production capacities of most industries
were limited, and were still not yet fully resumed. The satellite remote sensing technology can provide a new view to quantify the status
of industrial activities and public travel,which monitors variations of the heat emission from heavy industrial sectors with high-energy
consuming and the atmospheric NO2 mainly from industrial emissions and vehicles. For more details , please see the research progress
“Satellite observations of the return-to-work over China during the period of COVID-19” in volume 24, issue 7 (page 824-836).